GST Revenue Collection for April 2024
On a month-on-month basis, the collection of GST revenue for April 2024 has been the highest ever at Rs. 2.10 lakh crore. GST inflows register a remarkable breach of ₹2 lakh crore mark. Gross Revenue Records a 12.4% year-over-year increase. After a discount or refund, net revenue of ₹1,92,000 crores was achieved, which was 15.5 percent more than last year. There was a massive jump in the Gross GST Receipts to an unbelievable amount of ₹2.10 lakh crores last month. This figure is an impressive 12.4% higher year-over-year growth figure, and is mainly attributed to the strong domestic transaction rise (the domestic transaction base went up by 13.4%) and import influx increase (the import base grew by 8.3%). As Claim back is considered, GST Revenue with Net Sales value for April 2024 come in at ₹1,92,000 crore which has been a phenomenal 15.5% growth compared to 2022, where this amount was ₹1.65 lakh crore.
Breakdown of April 2024 Collections:
- Central Goods and Services Tax (CGST): ₹43,846 crore;
- State Goods and Services Tax (SGST): ₹53,538 crore;
- Integrated Goods and Services Tax (IGST): ₹99,623 crore, including ₹37,826 crore collected on imported goods;
- Cess: ₹13,260 crore, including ₹1,008 crore collected on imported goods.
Inter-Governmental Settlement
In the process of April 2024, the central government CGST accounts settled ₹50,307 crore and SGST accounts settled ₹41,600 crore. From IGST collections, these amounts were realized. In this case; it stands for the annual revenue from both CGST and SGST; which amounts to the total of 94153 crore for CGST and 95138 crore for SGST until the 1st of April, 2024 when there are regular settlements.
In March 2024, the Goods and Services Tax (GST) collection denoted the total amount of tax revenue gathered by the government from the sales of goods and services during that month. This figure reflects the financial health of the economy and provides insights into consumption patterns and business activities. Understanding GST collection helps policymakers make informed decisions to manage public finances effectively.
Exploring March 2024’s GST Collection

Let’s discuss the funds collected from the GST in March 2024 by the government. It is huge since it usually tells us a lot about the state of the economy.

The Ups and Downs: So what happened?
It all started well in March 2024. We were spending money, business was developing and everything seemed perfect. However, some strange issues had cropped up. Questions such as cargo backlogs, storms, and conflicts have been impeding businesses to continue.
What Are the Changes for Businesses?
These challenges caused the ripple effect. The businesses were unable to make much profit because they could not sell as much. That put pressure on them to stay profit-oriented.
What Is It for You that This Means?
When we see the consequences of March 2024, it is always obvious that it was not all roses for businesses. On the other side of the coin, it offers them the opportunity to consider new methods and come back as a stronger person.
What Should We Prepare For?
We can conclude that the future belongs to smart and flexible businesses. They must engage technology, partner, and come up with fresh ideas, if they are to continue expanding. Also, it falls to the government to invent opportunities for enterprises to succeed.
Implications for Businesses and the Economy
The fluctuation in March 2024’s GST collection holds several implications for businesses and the overall economy: The fluctuation in March 2024’s GST collection holds several implications for businesses and the overall economy:
-
Cash Flow Management:
Businesses have to take into account the irregular cash outflows resulting from GST collections, to have a cash flow management that will run smoothly. Maintaining steady reserves ensured that the impact of the ups and downs of revenue was minimized.

-
Adaptability:
Confronted with a volatile economic setting, business entities need to be agile and responsive to consumers’ behaviors, market challenges and possible new regulations to maintain their growth, and avoid risks.
-
Government Intervention:
Governments could consider adjustment of policy provisions or strategies to guarantee companies’ continuity and development during the economic downtime, which could bring stability to the economy.
Factors Influencing March 2024’s GST Collection
Several factors can influence the GST collection for March 2024:Several factors can influence the GST collection for March 2024:
-
Economic Activity:
Economic activity consists of consumption, production and investment. The collection of GST depends upon their levels to a great extent.
-
Tax Compliance:
The degree of GST payment compliance among corporate entities and individuals represents the amounts of GST that the government collects.
-
Government Policies:
Changing the government policy towards the rate of GST, exemptions, and incentives has been found to affect the amount of income collected.
-
Seasonal Variations:
Some sectors will probably have years with a seasonal variation in sales, and that will inevitably impact the collection of GSTs.
March GST Collections
GST revenue collection increased to the second highest of the year in March at ₹1.78 lakh crores; Year on year Collections registered a 11.5% growth rate while on a net basis collections recorded an increase of 18.4%.
The collection of GST or the Goods and Services Tax in March 2024 at ₹1.78 lakh crore was the second highest after the first position was recorded in March 2019 at the same value, with an 11.5% year-on-year growth. The above mentioned tax surge was propelled by an impressive rise in GST collection from the transactions at the domestic level to 17.6%. Canceling the GST revenue, net of refunds, for March 2024 is 1.65 lakh crore, which is a growth of 18.4% compared to the same period of the previous year.
Strong Consistent Performance in FY 2023-24:
The GST collection continued to grow with FY 2023-24 achieving the major milestone of total gross GST collection of Rs. 20.Over ₹18 lakh crore which is equal to ₹22 lakh crore is the budgetary expenditures having an increase of 11.7% compared to the previous year’s expenditures. On average the collection during the present financial year is ₹1.68 lakh crore which is far beyond that of the last financial year- ₹1.5 lakh crore. The government of India has collected GST net of its refunds and current year
up to March 2024 is ₹18,01,000 crore with a growth rate of 13.4% rise in the same period in last year.

Breakdown of March 2024 Collections:
- Central Goods and Services Tax (CGST): ₹34,532 crore;
- State Goods and Services Tax (SGST): ₹43,746 crore;
- Integrated Goods and Services Tax (IGST): ₹87,947 crore, including ₹40,322 crore collected on imported goods;
- Cess: ₹12,259 crore, including ₹996 crore collected on imported goods.
Inter-Governmental Settlement
The month of March recorded the government settlement of Rs. 43,264 crores for CGST and Rs. 37,704 crores for SGST from the IGST collection for that particular month. This converts to the CGST revenue of ₹77,796 crore and SGST revenue of ₹81.450 crore sold in the month of March 2024 after regular settlement.
Trends in GST Collection
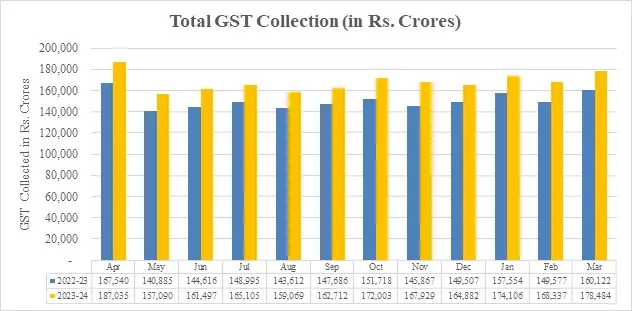
The Below chart reflects a movement in the monthly gross revenue GST during the current year. The statistics of GST collection state-wise from each State in March in the fiscal years 2024 and 2023 shown in Table
State-wise growth of GST Revenues during March 2024
| State/UT | Mar-23 | Mar-24 | Growth (%) |
| Jammu and Kashmir | 477 | 601 | 26% |
| Himachal Pradesh | 739 | 852 | 15% |
| Punjab | 1,735 | 2,090 | 20% |
| Chandigarh | 202 | 238 | 18% |
| Uttarakhand | 1,523 | 1,730 | 14% |
| Haryana | 7,780 | 9,545 | 23% |
| Delhi | 4,840 | 5,820 | 20% |
| Rajasthan | 4,154 | 4,798 | 15% |
| Uttar Pradesh | 7,613 | 9,087 | 19% |
| Bihar | 1,744 | 1,991 | 14% |
| Sikkim | 262 | 303 | 16% |
| Arunachal Pradesh | 144 | 168 | 16% |
| Nagaland | 58 | 83 | 43% |
| Manipur | 65 | 69 | 6% |
| Mizoram | 70 | 50 | -29% |
| Tripura | 90 | 121 | 34% |
| Meghalaya | 202 | 213 | 6% |
| Assam | 1,280 | 1,543 | 21% |
| West Bengal | 5,092 | 5,473 | 7% |
| Jharkhand | 3,083 | 3,243 | 5% |
| Odisha | 4,749 | 5,109 | 8% |
| Chhattisgarh | 3,017 | 3,143 | 4% |
| Madhya Pradesh | 3,346 | 3,974 | 19% |
| Gujarat | 9,919 | 11,392 | 15% |
| Dadra and Nagar Haveli and Daman & Diu | 309 | 452 | 46% |
| Maharashtra | 22,695 | 27,688 | 22% |
| Karnataka | 10,360 | 13,014 | 26% |
| Goa | 515 | 565 | 10% |
| Lakshadweep | 3 | 2 | -18% |
| Kerala | 2,354 | 2,598 | 10% |
| Tamil Nadu | 9,245 | 11,017 | 19% |
| Puducherry | 204 | 221 | 9% |
| Andaman and Nicobar Islands | 37 | 32 | -14% |
| Telangana | 4,804 | 5,399 | 12% |
| Andhra Pradesh | 3,532 | 4,082 | 16% |
| Ladakh | 23 | 41 | 82% |
| Other Territory | 249 | 196 | -21% |
| Center Jurisdiction | 142 | 220 | 55% |
Conclusion
The GST revenue collection in March of 2024 was full of ups and downs. At the outset, there was a sizable jump, which higher economic activity or improved tax compliance could entail. After the fact, it dropped abruptly causing us to question if the economic recovery is robust enough to sustain. This is a testament in favor of finding the right avenue of government spending and ensuring our economy has the ability to handle unexpected fluctuations. We must make a critical examination of the reasons for these ups and downs, so that we can be ready for any future tribulation that might come our way. Indeed, it is a tool for better thinking about how to keep our economy not only on track but also thriving.
Also Read: GST: Everything You Need To Know
FAQ
-
What is GST?
GST is the abbreviation of the Goods and Services Tax that is charged without any touch from the person using the goods and services. It is an indirect tax.
-
What does “From Boom to Bust” stance allude to on the matter of March 2024’s GST Collection?
It possibly alludes to a big decrease or a decrease in GST revenue in this specific situation of a time involving prosperity or growth and another situation of decline or recession.
-
What has made March 2024’s GST Collection deserve the special attention it has received?
The March 2024 GST Complete data can be a gauge of the overall health of the economy, and it is a vital report on the extent to which the economy is growing or declining.
-
What was behind the growing rise in GST revenue till March 2024?
These factors may hold true in putting more money in circulation, higher consumption levels, better tax compliance, or a change in tax policy.
-
What could be the various factors for the lowering shown by the GST collection in March 2024?
The reasons could be linked with economic slowdown, lower demand, deviant consumer behavior, policy variance affecting productiveness in local businesses, or external factors like the global economic situation.
-
Does the GST Collection of March 2024 differ from one month or the other of last session?
We may see a kind of analogy that can help us follow the overall economic trend and how the effectiveness of tax policies vary over time.

-
What exactly are the areas or departments that experience the decrease in GST collecting?
Some spheres like retail, hospitality, manufacturing or services may suffer the most from being tightened by GST accounts keeping.
-
Which actions are countries planning to undertake to stabilize the rate of GST collection?
Governments may act by policy, fiscal or incentives plans to increase spending and consumption due to the fact of economic slowdown.
-
If the GST collection does drop after the end of the stimulus, how would the economy be influenced in the long-run?
The extended consequences by this time could be reactions on GDP growth, employment rates, inflation, government revenue, and an overall economic stability.
-
The business and consumer who are the main part of the GST process reconsider their behavior now due to the changing collection landscape?
Businesses should take a time out to evaluate their approaches, ensure and continue with cash flow management, and keep up with changing market scenarios. Shoppers may decide to minimize their consumption or at least alter their spending habits in response.

